Best IR Sensor for IoT Projects – Types, Working, Interfacing, and Applications Explained
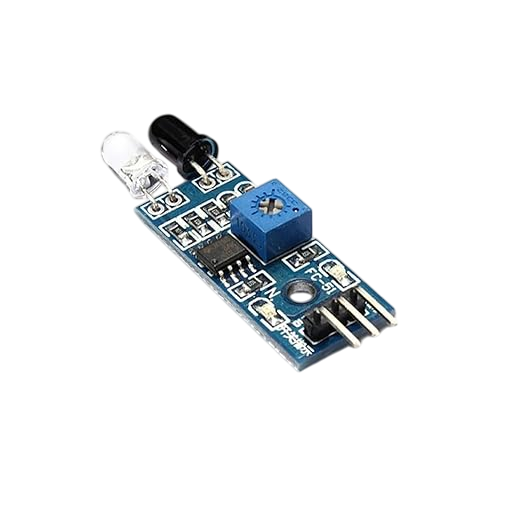
Overview
Introduction
An IR (Infrared) Sensor is an electronic device that detects infrared radiation from its surroundings. It is widely used in automation, obstacle detection, motion sensing, line following robots, and various electronic projects. IR sensors are compact, affordable, and easy to integrate into microcontroller-based systems.
This guide explains everything you need to know about IR sensors — their types, working principle, interfacing techniques, and real-world examples — to help you understand how IR technology enhances electronics and automation.What is an IR Sensor?
An IR sensor is a device that detects infrared light emitted by objects. It operates in the infrared region (typically 700 nm to 1 mm) of the electromagnetic spectrum. IR sensors are commonly used to measure heat or detect motion. These sensors work based on two components:-
IR Transmitter (usually an IR LED) – emits infrared radiation.
-
IR Receiver (usually a photodiode or phototransistor) – receives reflected IR radiation.
How Does an IR Sensor Work?
IR sensors follow a simple working principle:-
The IR LED emits infrared light continuously.
- If an object comes in front of the sensor, the light reflects back.
-
The photodiode or phototransistor detects the reflected IR beam.
- Based on the signal, the sensor module generates HIGH or LOW output (digital IR sensor), or varying analog output (analog IR sensor).
Types of IR Sensors
IR sensors are mainly categorized into the following types:1. Active IR Sensor
- Has both transmitter and receiver.
- Emits IR beam and detects its reflection.
- Used in motion detectors, distance measuring, obstacle sensing.
- Example: IR obstacle sensor module.
2. Passive IR Sensor (PIR Sensor)
- Only detects emitted infrared radiation from heat sources (like humans or animals).
- No IR beam emission involved.
- Used in security systems and motion sensing.
- Example: PIR motion sensor.
3. Analog IR Sensor
- Gives continuous voltage output based on distance.
- Output changes with proximity.
- Suitable for precision distance measuring.
4. Digital IR Sensor
- Gives only two outputs: HIGH or LOW.
- Used in basic obstacle sensing.
- Very commonly used with Arduino and embedded boards.
Key Features of IR Sensors
- Low power consumption
- Compact size
- Affordable and widely available
- Non-contact detection
- Reliable for close-range object detection
- Simple interfacing with microcontrollers (Arduino, ESP32, etc.)
IR Sensor Applications
IR sensors are used in various fields and industries:-
Smart electronics – Touchless switches, IR remotes
-
Robotics – Obstacle avoidance, line following robots
-
Security systems – Intrusion detection using PIR sensors
-
Industrial automation – Object counter, conveyor belt sensing
-
Consumer electronics – TV remotes, smart fans, gesture controls
-
Home automation – Automatic lighting systems
Interfacing IR Sensor with Microcontroller (Example)
Let’s take an example of interfacing an IR obstacle sensor module with Arduino Uno:
Components Required:
- Arduino Uno
- IR Sensor Module
- LED
- Jumper Wires
- Breadboard
Connection:
-
IR Sensor VCC → Arduino 5V
-
IR Sensor GND → Arduino GND
-
IR Sensor OUT → Arduino Digital Pin 2
-
LED Anode → Arduino Pin 13
-
LED Cathode → GND
Output:
- When an object is detected, LED turns ON and "Obstacle Detected" is printed.
- When no object is near, LED remains OFF and "Clear" is printed.
Advantages of IR Sensors
- Contactless detection increases durability
- Cost-effective for commercial and DIY use
- Versatile usage in embedded and automation systems
- Quick response and high sensitivity
- Easy to program and interface
Disadvantages of IR Sensors
- Limited detection range (usually < 30 cm for basic modules)
- Affected by ambient sunlight and reflections
- Not ideal for long-distance detection
Buying Guide – How to Choose the Right IR Sensor?
-
Purpose: Use PIR for motion detection, active IR for obstacle sensing.
-
Range: Choose based on required detection distance.
-
Output type: Analog vs Digital based on your application.
-
Compatibility: Check voltage and signal compatibility with microcontroller.
-
Ambient environment: For outdoor use, prefer sensors with better filtering.
Where to Buy
Prices may vary. Click on "Buy Now" to check current availability and pricing.
Administrator
Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions about Best IR Sensor for IoT Projects – Types, Working, Interfacing, and Applications Explained. Find answers to the most frequently asked questions.
User Reviews & Comments
Share your experience with this IoT Blog. Your feedback helps our community make informed decisions!
Share Your Experience
Help others by sharing your thoughts about this IoT Blog.
Related Blogs
Explore more IoT Blogs in the same category
Ultrasonic Sensor HC-SR04 for IoT: Working, Applications, Circuit, and Integration Guide
Sensors
Discover how the Ultrasonic Sensor HC-SR04 works and how to use it in IoT projects. This detailed guide covers its working principle, pin configuration, interfacing with Arduino, applications in smart systems, and complete circuit setup. Ideal for beginners and IoT developers looking to integrate distance sensing in real-time projects.

Vibration Sensor: Working, Types, Applications, and Complete Guide
Sensors
A vibration sensor is a crucial device used to detect and measure vibrations in machines, structures, and environments. This complete guide covers how vibration sensors work, their different types, applications across industries, and factors to consider before selection. Learn how these sensors improve safety, enhance performance, and prevent costly equipment failures.

What is a Photoresistor (LDR) in IoT? Working, Applications & Circuit Examples Explained
Sensors
Discover how photoresistors (LDRs) work in IoT projects. Learn about their functions, real-world applications, circuit integration, and why they are essential in modern smart systems. This detailed guide helps electronics and IoT enthusiasts understand light sensors and their role in automation. Perfect for students, hobbyists, and developers looking to build smarter, light-based solutions.
No Reviews Yet
Be the first to share your experience with this IoT Blog!